Oral lichen planus (OLP) is an inflammatory condition affecting the lining of the mouth. It occurs most often inside the cheeks, but it can affect the gums, tongue, lips and other parts of the mouth. Occasionally it is found in the throat.
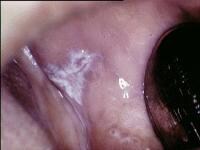
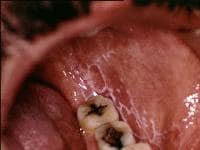
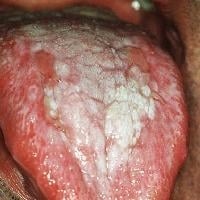
OLP commonly causes lacy white patches or raised red mouth sores or ulcers. Some patients have no symptoms, while others experience:
- Painful burning sensations
- Dry mouth
- A metallic taste in the mouth
- Painful, open sores
An initial episode of OLP may last for weeks or months and recurrences may continue over many years. OLP affects approximately 1 percent to 2 percent of the population. It usually appears between age 45 and 60, but can occur at any age. Women are twice as likely to get it than men. OLP rarely affects children.
The cause of OLP isn't certain. It is not an infectious disease and it is not contagious. It can be triggered by an allergic reaction to drugs or to chemicals or dental materials touching the mucosal lining of the mouth. Often the source of symptoms can't be determined.
Plaquelike oral lichen planus on the buccal mucosa on the left side.
Reticular oral lichen planus on the buccal mucosa on the left side
Ulcerative oral lichen planus on the dorsum of the tongue.